Internal linking
Fact: A website has a maximum amount of PageRank that is distributed between its pages by internal links.
The maximum PageRank in a site equals the number of pages in the site * 1. The maximum is increased by inbound links from other sites and decreased by outbound links to other sites. We are talking about the overall PageRank in the site and not the PageRank of any individual page. You don't have to take my word for it. You can reach the same conclusion by using a pencil and paper and the equation.
Fact: The maximum amount of PageRank in a site increases as the number of pages in the site increases.
The more pages that a site has, the more PageRank it has. Again, by using a pencil and paper and the equation, you can come to the same conclusion. Bear in mind that the only pages that count are the ones that Google knows about.
Fact: By linking poorly, it is possible to fail to reach the site's maximum PageRank, but it is not possible to exceed it.
Poor internal linkages can cause a site to fall short of its maximum but no kind of internal link structure can cause a site to exceed it. The only way to increase the maximum is to add more inbound links and/or increase the number of pages in the site.
Cautions: Whilst I thoroughly recommend creating and adding new pages to increase a site's total PageRank so that it can be channeled to specific pages, there are certain types of pages that should not be added. These are pages that are all identical or very nearly identical and are known as cookie-cutters. Google considers them to be spam and they can trigger an alarm that causes the pages, and possibly the entire site, to be penalized. Pages full of good content are a must.
What can we do with this 'overall' PageRank?
We are going to look at some example calculations to see how a site's PageRank can be manipulated, but before doing that, I need to point out that a page will be included in the Google index only if one or more pages on the web link to it. That's according to Google. If a page is not in the Google index, any links from it can't be included in the calculations.
For the examples, we are going to ignore that fact, mainly because other 'Pagerank Explained' type documents ignore it in the calculations, and it might be confusing when comparing documents. The calculator operates in two modes:- Simple and Real. In Simple mode, the calculations assume that all pages are in the Google index, whether or not any other pages link to them. In Real mode the calculations disregard unlinked-to pages. These examples show the results as calculated in Simple mode. pagerank, page rank
Let's consider a 3 page site (pages A, B and C) with no links coming in from the outside. We will allocate each page an initial PageRank of 1, although it makes no difference whether we start each page with 1, 0 or 99. Apart from a few millionths of a PageRank point, after many iterations the end result is always the same. Starting with 1 requires fewer iterations for the PageRanks to converge to a suitable result than when starting with 0 or any other number. You may want to use a pencil and paper to follow this or you can follow it with the calculator.
The site's maximum PageRank is the amount of PageRank in the site. In this case, we have 3 pages so the site's maximum is 3.
At the moment, none of the pages link to any other pages and none link to them. If you make the calculation once for each page, you'll find that each of them ends up with a PageRank of 0.15. No matter how many iterations you run, each page's PageRank remains at 0.15. The total PageRank in the site = 0.45, whereas it could be 3. The site is seriously wasting most of its potential PageRank.
Example 1:
Now begin again with each page being allocated PR1. Link page A to page B and run the calculations for each page. We end up with:-
Page A = 0.15
Page B = 1
Page C = 0.15
Page A has "voted" for page B and, as a result, page B's PageRank has increased. This is looking good for page B, but it's only 1 iteration - we haven't taken account of the Catch 22 situation. Look at what happens to the figures after more iterations:-
After 100 iterations the figures are:-
Page A = 0.15
Page B = 0.2775
Page C = 0.15
It still looks good for page B but nowhere near as good as it did. These figures are more realistic. The total PageRank in the site is now 0.5775 - slightly better but still only a fraction of what it could be.
NOTE:
Technically, these particular results are incorrect because of the special treatment that Google gives to dangling links, but they serve to demonstrate the simple calculation.
Example 2:
Try this linkage. Link all pages to all pages. Each page starts with PR1 again. This produces:-
Page A = 1
Page B = 1
Page C = 1
Now we've achieved the maximum. No matter how many iterations are run, each page always ends up with PR1. The same results occur by linking in a loop. E.g. A to B, B to C and C to D. View this in the calculator.
This has demonstrated that, by poor linking, it is quite easy to waste PageRank and by good linking, we can achieve a site's full potential. But we don't particularly want all the site's pages to have an equal share. We want one or more pages to have a larger share at the expense of others. The kinds of pages that we might want to have the larger shares are the index page, hub pages and pages that are optimized for certain search terms. We have only 3 pages, so we'll channel the PageRank to the index page - page A. It will serve to show the idea of channeling.
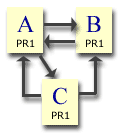
Example 3:
Now try this. Link page A to both B and C. Also link pages B and C to A. Starting with PR1 all round, after 1 iteration the results are:-
Page A = 1.85
Page B = 0.575
Page C = 0.575
and after 100 iterations, the results are:-
Page A = 1.459459
Page B = 0.7702703
Page C = 0.7702703
In both cases the total PageRank in the site is 3 (the maximum) so none is being wasted. Also in both cases you can see that page A has a much larger proportion of the PageRank than the other 2 pages. This is because pages B and C are passing PageRank to A and not to any other pages. We have channeled a large proportion of the site's PageRank to where we wanted it.
Example 4:
Finally, keep the previous links and add a link from page C to page B. Start again with PR1 all round. After 1 iteration:-
Page A = 1.425
Page B = 1
Page C = 0.575
By comparison to the 1 iteration figures in the previous example, page A has lost some PageRank, page B has gained some and page C stayed the same. Page C now shares its "vote" between A and B. Previously A received all of it. That's why page A has lost out and why page B has gained. and after 100 iterations:-
Page A = 1.298245
Page B = 0.9999999
Page C = 0.7017543
When the dust has settled, page C has lost a little PageRank because, having now shared its vote between A and B, instead of giving it all to A, A has less to give to C in the A-->C link. So adding an extra link from a page causes the page to lose PageRank indirectly if any of the pages that it links to return the link. If the pages that it links to don't return the link, then no PageRank loss would have occured. To make it more complicated, if the link is returned even indirectly (via a page that links to a page that links to a page etc), the page will lose a little PageRank. This isn't really important with internal links, but it does matter when linking to pages outside the site.
Example 5: new pages
Adding new pages to a site is an important way of increasing a site's total PageRank because each new page will add an average of 1 to the total. Once the new pages have been added, their new PageRank can be channeled to the important pages. We'll use the calculator to demonstrate these.
Let's add 3 new pages to Example 3 [view]. Three new pages but they don't do anything for us yet. The small increase in the Total, and the new pages' 0.15, are unrealistic as we shall see. So let's link them into the site.
Link each of the new pages to the important page, page A [view]. Notice that the Total PageRank has doubled, from 3 (without the new pages) to 6. Notice also that page A's PageRank has almost doubled.
There is one thing wrong with this model. The new pages are orphans. They wouldn't get into Google's index, so they wouldn't add any PageRank to the site and they wouldn't pass any PageRank to page A. They each need to be linked to from at least one other page. If page A is the important page, the best page to put the links on is, surprisingly, page A [view]. You can play around with the links but, from page A's point of view, there isn't a better place for them.
It is not a good idea for one page to link to a large number of pages so, if you are adding many new pages, spread the links around. The chances are that there is more than one important page in a site, so it is usually suitable to spread the links to and from the new pages. You can use the calculator to experiment with mini-models of a site to find the best links that produce the best results for its important pages.
Examples summary:
You can see that, by organising the internal links, it is possible to channel a site's PageRank to selected pages. Internal links can be arranged to suit a site's PageRank needs, but it is only useful if Google knows about the pages, so do try to ensure that Google spiders them.
Inbound and Outbound links:
Examples of these could be given but it is probably clearer to read about them (below) and to 'play' with them in the calculator.
Questions:
When a page has several links to another page, are all the links counted?
E.g. if page A links once to page B and 3 times to page C, does page C receive 3/4 of page A's shareable PageRank?
The PageRank concept is that a page casts votes for one or more other pages. Nothing is said in the original PageRank document about a page casting more than one vote for a single page. The idea seems to be against the PageRank concept and would certainly be open to manipulation by unrealistically proportioning votes for target pages. E.g. if an outbound link, or a link to an unimportant page, is necessary, add a bunch of links to an important page to minimize the effect.
Since we are unlikely to get a definitive answer from Google, it is reasonable to assume that a page can cast only one vote for another page, and that additional votes for the same page are not counted.
When a page links to itself, is the link counted?
Again, the concept is that pages cast votes for other pages. Nothing is said in the original document about pages casting votes for themselves. The idea seems to be against the concept and, also, it would be another way to manipulate the results. So, for those reasons, it is reasonable to assume that a page can't vote for itself, and that such links are not counted.
Dangling links
pagerank, page rank "Dangling links are simply links that point to any page with no outgoing links. They affect the model because it is not clear where their weight should be distributed, and there are a large number of them. Often these dangling links are simply pages that we have not downloaded yet..........Because dangling links do not affect the ranking of any other page directly, we simply remove them from the system until all the PageRanks are calculated. After all the PageRanks are calculated they can be added back in without affecting things significantly." - extract from the original PageRank paper by Google’s founders, Sergey Brin and Lawrence Page.
A dangling link is a link to a page that has no links going from it, or a link to a page that Google hasn't indexed. In both cases Google removes the links shortly after the start of the calculations and reinstates them shortly before the calculations are finished. In this way, their effect on the PageRank of other pages in minimal.
The results shown in Example 1 (right diag.) are wrong because page B has no links going from it, and so the link from page A to page B is dangling and would be removed from the calculations. The results of the calculations would show all three pages as having 0.15.
It may suit site functionality to link to pages that have no links going from them without losing any PageRank from the other pages but it would be waste of potential PageRank. Take a look at this example. The site's potential is 5 because it has 5 pages, but without page E linked in, the site only has 4.15.
Link page A to page E and click Calculate. Notice that the site's total has gone down very significantly. But, because the new link is dangling and would be removed from the calculations, we can ignore the new total and assume the previous 4.15 to be true. That's the effect of functionally useful, dangling links in the site. There's no overall PageRank loss.
However, some of the site's potential total is still being wasted, so link Page E back to Page A and click Calculate. Now we have the maximum PageRank that is possible with 5 pages. Nothing is being wasted.
Although it may be functionally good to link to pages within the site without those pages linking out again, it is bad for PageRank. It is pointless wasting PageRank unnecessarily, so always make sure that every page in the site links out to at least one other page in the site.
[TOP]
Inbound links
Inbound links (links into the site from the outside) are one way to increase a site's total PageRank. The other is to add more pages. Where the links come from doesn't matter. Google recognizes that a webmaster has no control over other sites linking into a site, and so sites are not penalized because of where the links come from. There is an exception to this rule but it is rare and doesn't concern this article. It isn't something that a webmaster can accidentally do.
The linking page's PageRank is important, but so is the number of links going from that page. For instance, if you are the only link from a page that has a lowly PR2, you will receive an injection of 0.15 + 0.85(2/1) = 1.85 into your site, whereas a link from a PR8 page that has another 99 links from it will increase your site's PageRank by 0.15 + 0.85(7/100) = 0.2095. Clearly, the PR2 link is much better - or is it? See here for a probable reason why this is not the case.
Once the PageRank is injected into your site, the calculations are done again and each page's PageRank is changed. Depending on the internal link structure, some pages' PageRank is increased, some are unchanged but no pages lose any PageRank.
It is beneficial to have the inbound links coming to the pages to which you are channeling your PageRank. A PageRank injection to any other page will be spread around the site through the internal links. The important pages will receive an increase, but not as much of an increase as when they are linked to directly. The page that receives the inbound link, makes the biggest gain.
It is easy to think of our site as being a small, self-contained network of pages. When we do the PageRank calculations we are dealing with our small network. If we make a link to another site, we lose some of our network's PageRank, and if we receive a link, our network's PageRank is added to. But it isn't like that. For the PageRank calculations, there is only one network - every page that Google has in its index. Each iteration of the calculation is done on the entire network and not on individual websites.
Because the entire network is interlinked, and every link and every page plays its part in each iteration of the calculations, it is impossible for us to calculate the effect of inbound links to our site with any realistic accuracy.
[TOP]
Outbound links
Outbound links are a drain on a site's total PageRank. They leak PageRank. To counter the drain, try to ensure that the links are reciprocated. Because of the PageRank of the pages at each end of an external link, and the number of links out from those pages, reciprocal links can gain or lose PageRank. You need to take care when choosing where to exchange links.
When PageRank leaks from a site via a link to another site, all the pages in the internal link structure are affected. (This doesn't always show after just 1 iteration). The page that you link out from makes a difference to which pages suffer the most loss. Without a program to perform the calculations on specific link structures, it is difficult to decide on the right page to link out from, but the generalization is to link from the one with the lowest PageRank.
Many websites need to contain some outbound links that are nothing to do with PageRank. Unfortunately, all 'normal' outbound links leak PageRank. But there are 'abnormal' ways of linking to other sites that don't result in leaks. PageRank is leaked when Google recognizes a link to another site. The answer is to use links that Google doesn't recognize or count. These include form actions and links contained in javascript code.
Form actions
A form's 'action' attribute does not need to be the url of a form parsing script. It can point to any html page on any site. Try it.
Example:
<form name="myform" action="http://www.domain.com/somepage.html">
<a href="javascript:document.myform.submit()">Click here</a>
To be really sneaky, the action attribute could be in some javascript code rather than in the form tag, and the javascript code could be loaded from a 'js' file stored in a directory that is barred to Google's spider by the robots.txt file.
Javascript
Example: <a href="javascript:goto('wherever')">Click here</a>
Like the form action, it is sneaky to load the javascript code, which contains the urls, from a seperate 'js' file, and sneakier still if the file is stored in a directory that is barred to googlebot by the robots.txt file.
The "rel" attribute
As of 18th January 2005, Google, together with other search engines, is recognising a new attribute to the anchor tag. The attribute is "rel", and it is used as follows:-
<a href="http://www.domain.com/somepage.html" rel="nofollow">link text</a>
The attribute tells Google to ignore the link completely. The link won't help the target page's PageRank, and it won't help its rankings. It is as though the link doesn't exist. With this attribute, there is no longer any need for javascript, forms, or any other method of hiding links from Google.
[TOP]
So how much additional PageRank do we need to move up the toolbar?
First, let me explain in more detail why the values shown in the Google toolbar are not the actual PageRank figures. According to the equation, and to the creators of Google, the billions of pages on the web average out to a PageRank of 1.0 per page. So the total PageRank on the web is equal to the number of pages on the web * 1, which equals a lot of PageRank spread around the web.
The Google toolbar range is from 1 to 10. (They sometimes show 0, but that figure isn't believed to be a PageRank calculation result). What Google does is divide the full range of actual PageRanks on the web into 10 parts - each part is represented by a value as shown in the toolbar. So the toolbar values only show what part of the overall range a page's PageRank is in, and not the actual PageRank itself. The numbers in the toolbar are just labels.
Whether or not the overall range is divided into 10 equal parts is a matter for debate - Google aren't saying. But because it is much harder to move up a toolbar point at the higher end than it is at the lower end, many people (including me) believe that the divisions are based on a logarithmic scale, or something very similar, rather than the equal divisions of a linear scale.
Let's assume that it is a logarithmic, base 10 scale, and that it takes 10 properly linked new pages to move a site's important page up 1 toolbar point. It will take 100 new pages to move it up another point, 1000 new pages to move it up one more, 10,000 to the next, and so on. That's why moving up at the lower end is much easier that at the higher end.
In reality, the base is unlikely to be 10. Some people think it is around the 5 or 6 mark, and maybe even less. Even so, it still gets progressively harder to move up a toolbar point at the higher end of the scale.
Note that as the number of pages on the web increases, so does the total PageRank on the web, and as the total PageRank increases, the positions of the divisions in the overall scale must change. As a result, some pages drop a toolbar point for no 'apparent' reason. If the page's actual PageRank was only just above a division in the scale, the addition of new pages to the web would cause the division to move up slightly and the page would end up just below the division. Google's index is always increasing and they re-evaluate each of the pages on more or less a monthly basis. It's known as the "Google dance". When the dance is over, some pages will have dropped a toolbar point. A number of new pages might be all that is needed to get the point back after the next dance.
The toolbar value is a good indicator of a page's PageRank but it only indicates that a page is in a certain range of the overall scale. One PR5 page could be just above the PR5 division and another PR5 page could be just below the PR6 division - almost a whole division (toolbar point) between them.
[TOP]
Tips
Domain names and Filenames
To a spider, www.domain.com/, domain.com/, www.domain.com/index.html and domain.com/index.html are different urls and, therefore, different pages. Surfers arrive at the site's home page whichever of the urls are used, but spiders see them as individual urls, and it makes a difference when working out the PageRank. It is better to standardize the url you use for the site's home page. Otherwise each url can end up with a different PageRank, whereas all of it should have gone to just one url.
If you think about it, how can a spider know the filename of the page that it gets back when requesting www.domain.com/ ? It can't. The filename could be index.html, index.htm, index.php, default.html, etc. The spider doesn't know. If you link to index.html within the site, the spider could compare the 2 pages but that seems unlikely. So they are 2 urls and each receives PageRank from inbound links. Standardizing the home page's url ensures that the Pagerank it is due isn't shared with ghost urls.
Example: Go to my UK Holidays and UK Holiday Accommodation site - how's that for a nice piece of link text ;). Notice that the url in the browser's address bar contains "www.". If you have the Google Toolbar installed, you will see that the page has PR5. Now remove the "www." part of the url and get the page again. This time it has PR1, and yet they are the same page. Actually, the PageRank is for the unseen frameset page.
When this article was first written, the non-www URL had PR4 due to using different versions of the link URLs within the site. It had the effect of sharing the page's PageRank between the 2 pages (the 2 versions) and, therefore, between the 2 sites. That's not the best way to do it. Since then, I've tidied up the internal linkages and got the non-www version down to PR1 so that the PageRank within the site mostly stays in the "www." version, but there must be a site somewhere that links to it without the "www." that's causing the PR1.
Imagine the page, www.domain.com/index.html. The index page contains links to several relative urls; e.g. products.html and details.html. The spider sees those urls as www.domain.com/products.html and www.domain.com/details.html. Now let's add an absolute url for another page, only this time we'll leave out the "www." part - domain.com/anotherpage.html. This page links back to the index.html page, so the spider sees the index pages as domain.com/index.html. Although it's the same index page as the first one, to a spider, it is a different page because it's on a different domain. Now look what happens. Each of the relative urls on the index page is also different because it belongs to the domain.com/ domain. Consequently, the link stucture is wasting a site's potential PageRank by spreading it between ghost pages.
Adding new pages
There is a possible negative effect of adding new pages. Take a perfectly normal site. It has some inbound links from other sites and its pages have some PageRank. Then a new page is added to the site and is linked to from one or more of the existing pages. The new page will, of course, aquire PageRank from the site's existing pages. The effect is that, whilst the total PageRank in the site is increased, one or more of the existing pages will suffer a PageRank loss due to the new page making gains. Up to a point, the more new pages that are added, the greater is the loss to the existing pages. With large sites, this effect is unlikely to be noticed but, with smaller ones, it probably would.
So, although adding new pages does increase the total PageRank within the site, some of the site's pages will lose PageRank as a result. The answer is to link new pages is such a way within the site that the important pages don't suffer, or add sufficient new pages to make up for the effect (that can sometimes mean adding a large number of new pages), or better still, get some more inbound links.
[TOP]
Miscellaneous
The Google toolbar
If you have the Google toolbar installed in your browser, you will be used to seeing each page's PageRank as you browse the web. But all isn't always as it seems. Many pages that Google displays the PageRank for haven't been indexed in Google and certainly don't have any PageRank in their own right. What is happening is that one or more pages on the site have been indexed and a PageRank has been calculated. The PageRank figure for the site's pages that haven't been indexed is allocated on the fly - just for your toolbar. The PageRank itself doesn't exist.
It's important to know this so that you can avoid exchanging links with pages that really don't have any PageRank of their own. Before making exchanges, search for the page on Google to make sure that it is indexed.
Sub-directories
Some people believe that Google drops a page's PageRank by a value of 1 for each sub-directory level below the root directory. E.g. if the value of pages in the root directory is generally around 4, then pages in the next directory level down will be generally around 3, and so on down the levels. Other people (including me) don't accept that at all. Either way, because some spiders tend to avoid deep sub-directories, it is generally considered to be beneficial to keep directory structures shallow (directories one or two levels below the root).
ODP and Yahoo!
It used to be thought that Google gave a Pagerank boost to sites that are listed in the Yahoo! and ODP (a.k.a. DMOZ) directories, but these days general opinion is that they don't. There is certainly a PageRank gain for sites that are listed in those directories, but the reason for it is now thought to be this:-
Google spiders the directories just like any other site and their pages have decent PageRank and so they are good inbound links to have. In the case of the ODP, Google's directory is a copy of the ODP directory. Each time that sites are added and dropped from the ODP, they are added and dropped from Google's directory when they next update it. The entry in Google's directory is yet another good, PageRank boosting, inbound link. Also, the ODP data is used for searches on a myriad of websites - more inbound links!
Listings in the ODP are free but, because sites are reviewed by hand, it can take quite a long time to get in. The sooner a working site is submitted, the better. For tips on submitting to DMOZ, see this this DMOZ article.



Comments
Post a Comment